1. Crop acreage and production estimation:
Study Area: The district and Taluka level area and production estimations were carried out for Bagalkot and Belagavi districts of Karnataka state.
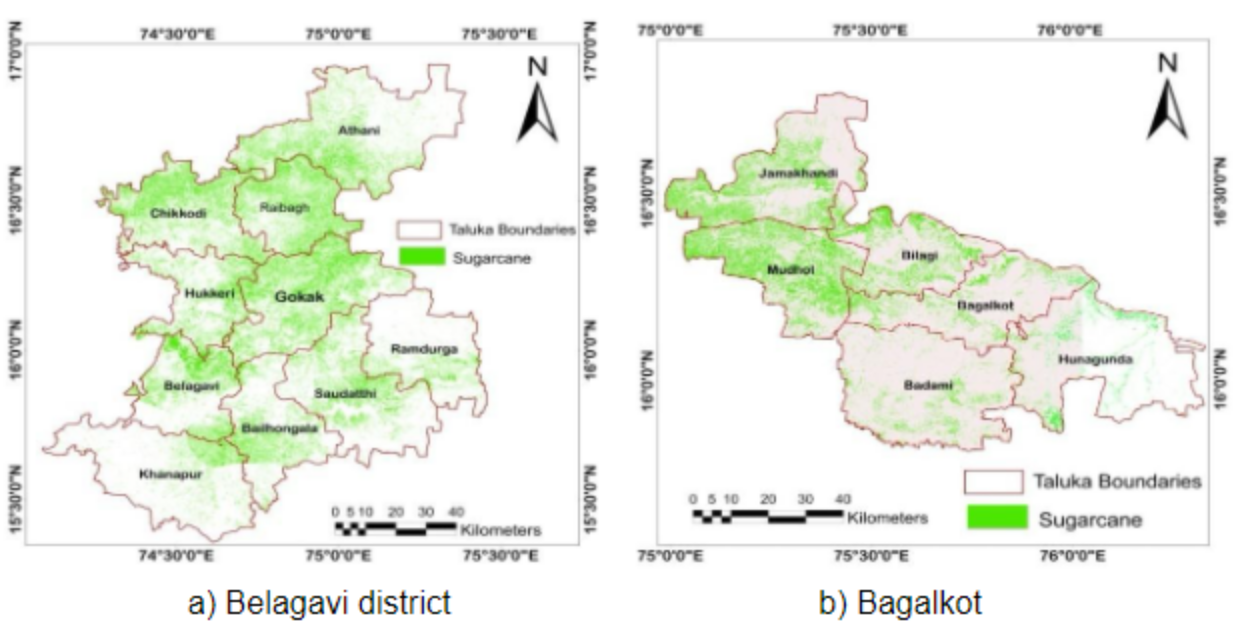
Sugarcane acreage map (Taluka-wise)
Taluka-wise sugarcane acreage comparison of Belagavi district KIAAR and Govt. of Karnataka 2020-21).
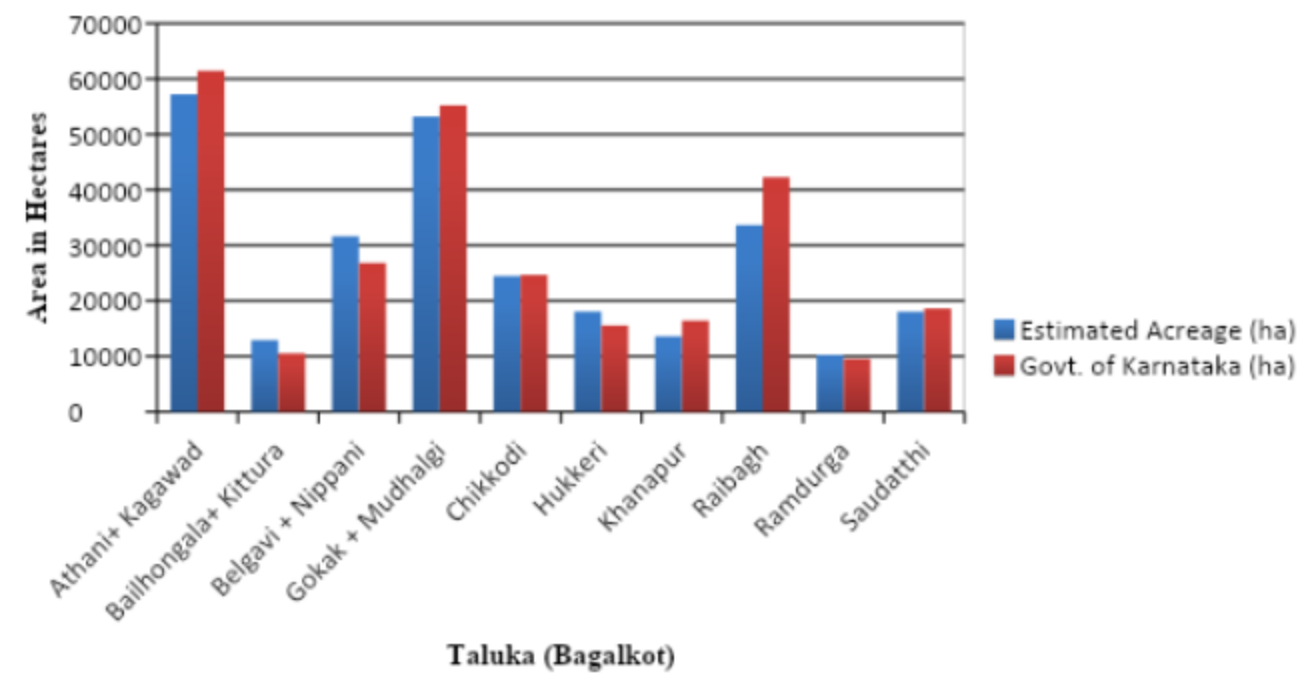
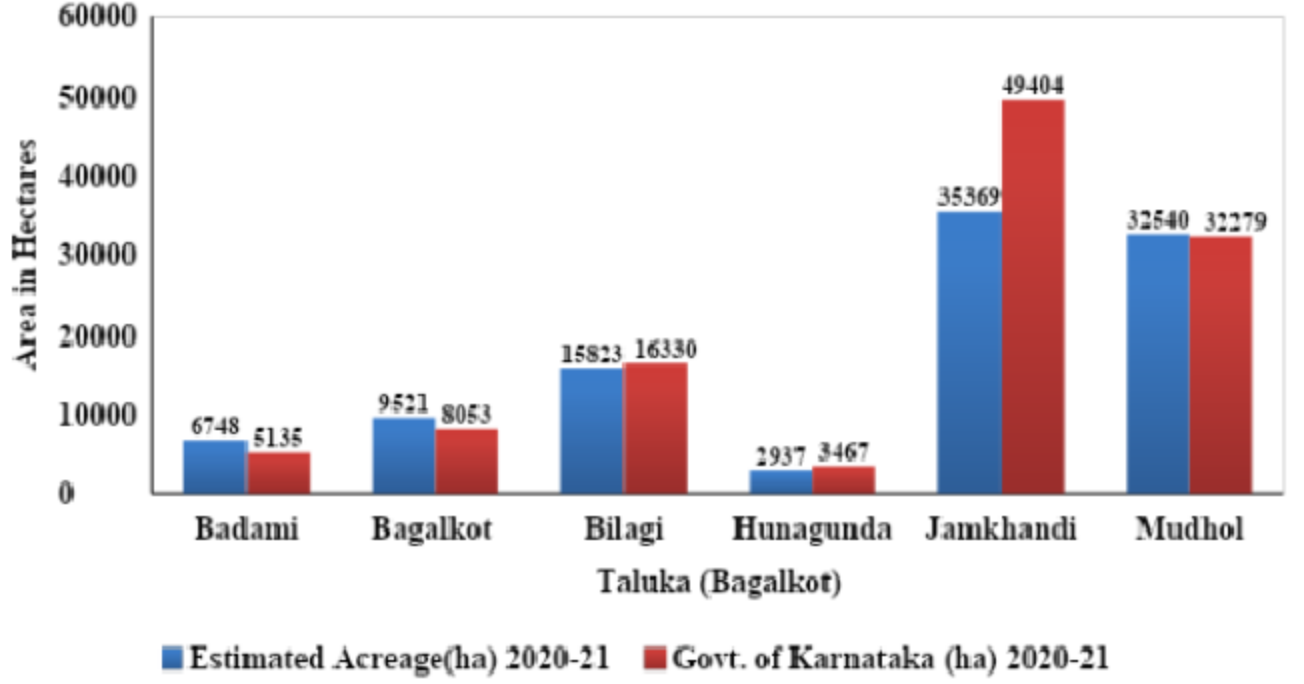
Taluka-wise sugarcane acreage comparison of Bagalkot district (KIAAR and Govt. of Karnataka 2020-21).
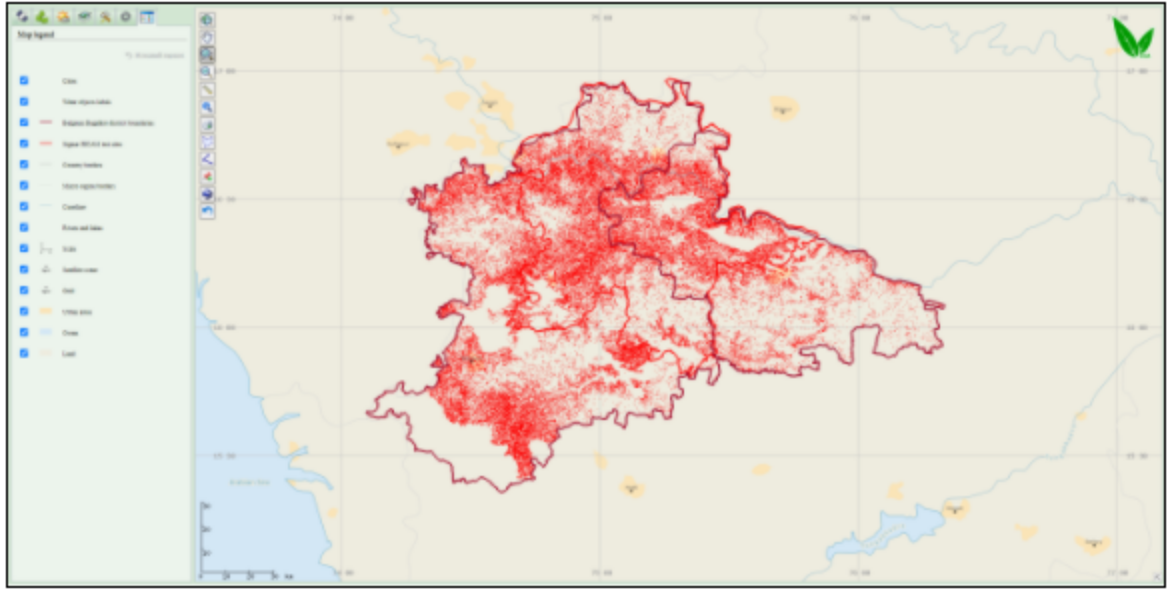
Sugarcane acreage estimation using Vega-Geoglam
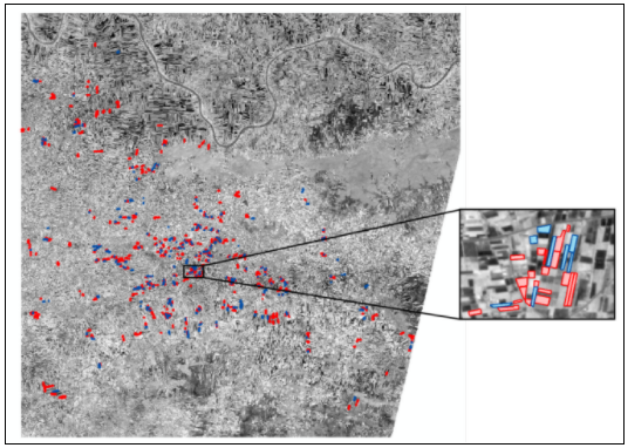
Sugarcane map (in red) for Bagalkot and Belgaum districts for 11.04.2020 in Vega-GEOGLAM interface. Zoomed in sugarcane map (in red) - There are in-situ information and Earth observation series of Sentinel-2A/B (MSI) and Sentinel-1 data for 2018-2020 available for the field

2. Sugarcane production estimation
Sugarcane Production map for Belagavi district (village-wise)
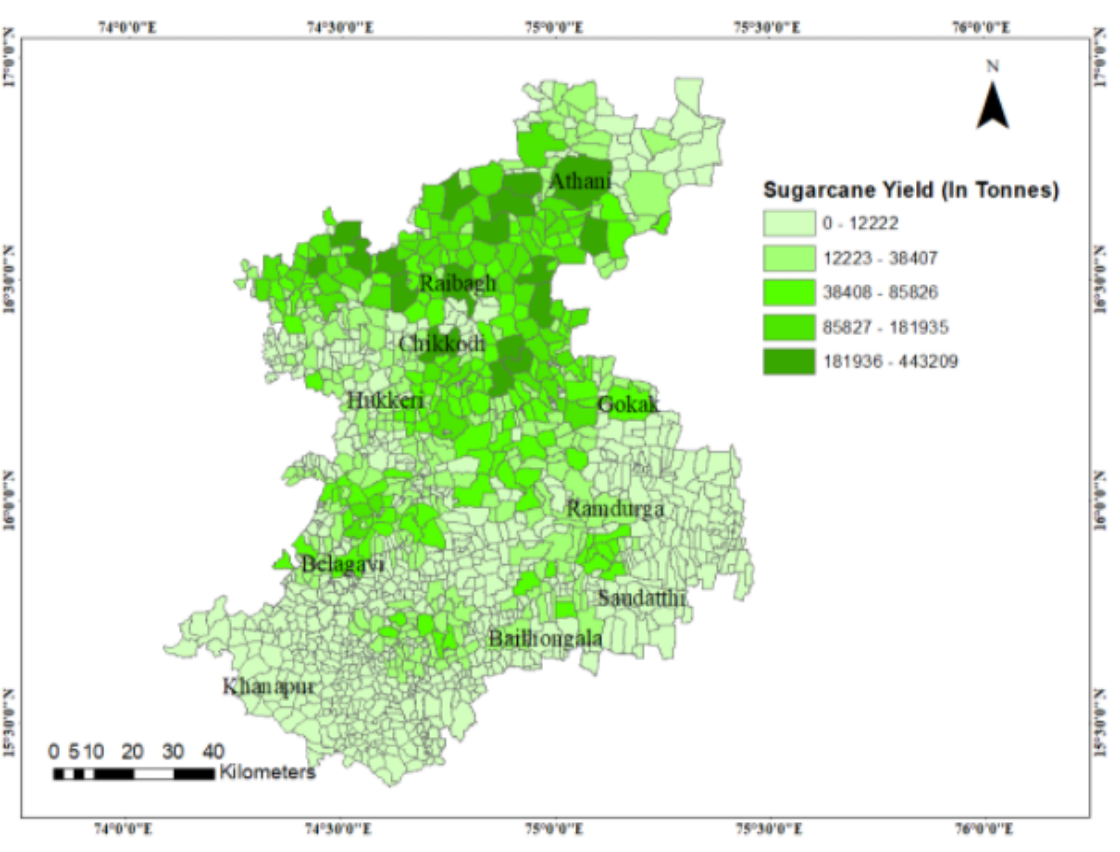
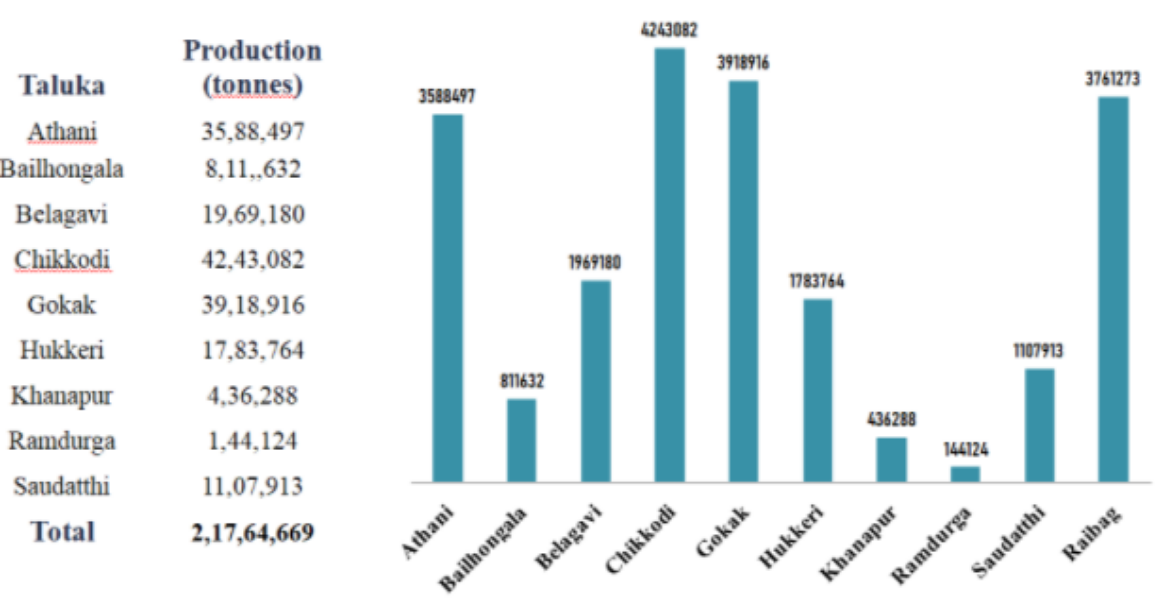
Estimated sugarcane production in Belagavi district (Taluka-wise)
3. Flood zone mapping:
Pre-Flood mapping using microwave remote sensing
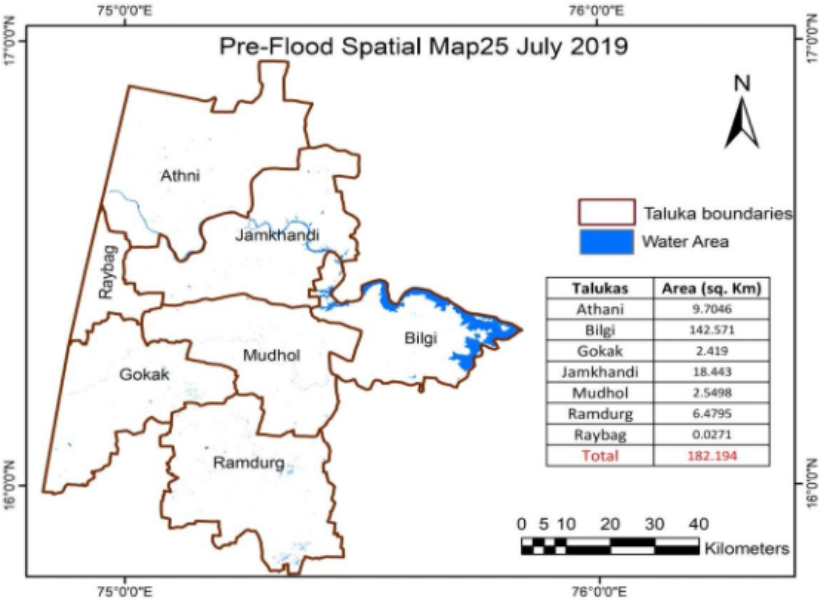
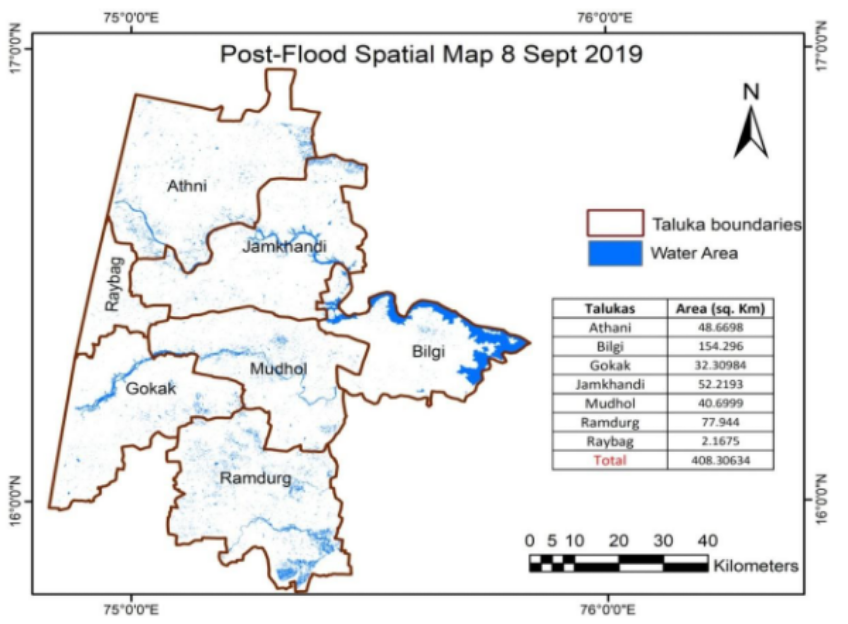
Post-Flood mapping using microwave remote sensing
4. Arable land mapping
Ground survey:
GPS handheld device (GARMIN MONTANA 680) was used for considering sugarcane homogenous plots at different phonological stages during the year 2019- 20. The ground data have been uploaded to VEGA-GEOGLAM to generate time-series NDVI composite images. The spectral and temporal profiles of the sugarcane crop were analyzed which helped us in separability of sugarcane with other crops.
724 Sugarcane samples were collected covering 2564.31 acres of land.
Samples were collected randomly from 61 villages of Bagalkot and Belgaum districts of Karnataka. More than six varieties of sugarcane were surveyedM265, CO 91010, C0 86032, PI1110, VSI8005, and SNK9293. Dominance of CO86032 and CO91010 varieties was observed in the region.
Corn, wheat and Turmeric samples were also collected. Total of 238 corn samples and 259 turmeric samples were collected covering 314.14 and 298.03 acres of land, respectively. These samples were collected randomly in Bagalkot and Belgaum districts.
These samples helped us in analyzing crop separability (crop classification) with different agronomic parameters e.g. crop type, crop variety, date of plantation, date of harvesting, intercropping, mixed cropping, soil type, irrigation type, and yield.
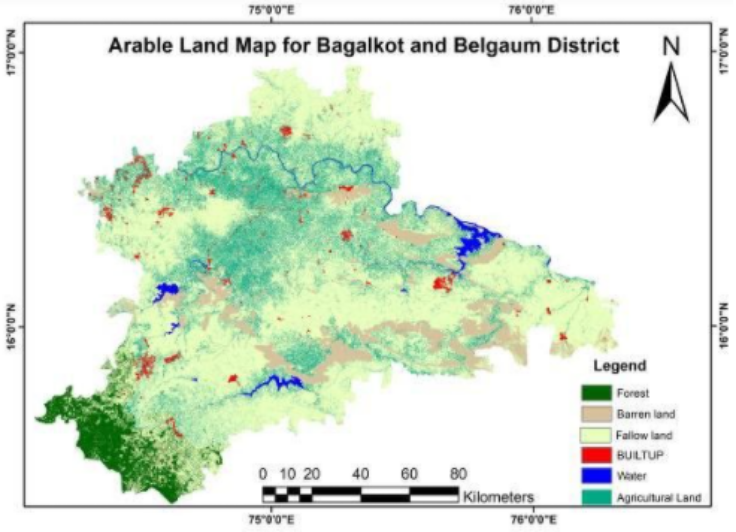
Arable land map
The sentinel-2 image was considered for extracting the arable lands. The image was broadly classified into 6 classes namely agricultural land, forest, waterbody, built-up, barren land and fallowland covering an area of 3392.97, 1099.91, 289.406, 266.501, 1845.23, and 12982.9,Sq.km, respectively.
The maximum likelihood classifier was adopted to classify the study area.
The overall accuracy was 86.69%
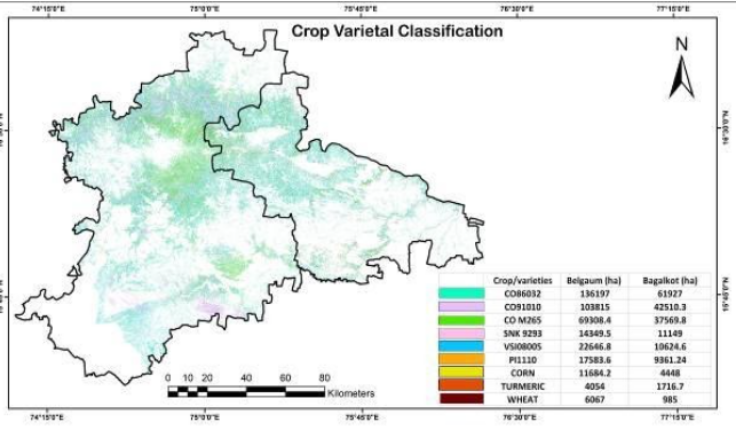
5.Crop varietal identification
Results showed overall classification accuracies of 85% for sugarcane crop classification and 80% for sugarcane varietal classification.
Among the sugarcane varieties, CO 86032 (Nayana) occupied the highest area covering 61927 and 136197 ha in Bagalkot and Belgaum districts, followed by Co 91010 (Dhanush) covering an area 42510.3 and 103815 ha in Bagalkot and Belgaum
Post-Flood mapping using microwave remote sensing
6.Sugarcane phenology classification
Sugarcane undergoes four growing phases i.e.
1. Germination phase,
2. Tillering (formative) phase
3. Grand growth phase
4. Maturity and ripening phase.
Plot level: four spectral bands i.e. Near Infrared (NIR), Red, Green, and Blue of Sentinel-2 satellite were stacked for the classification.
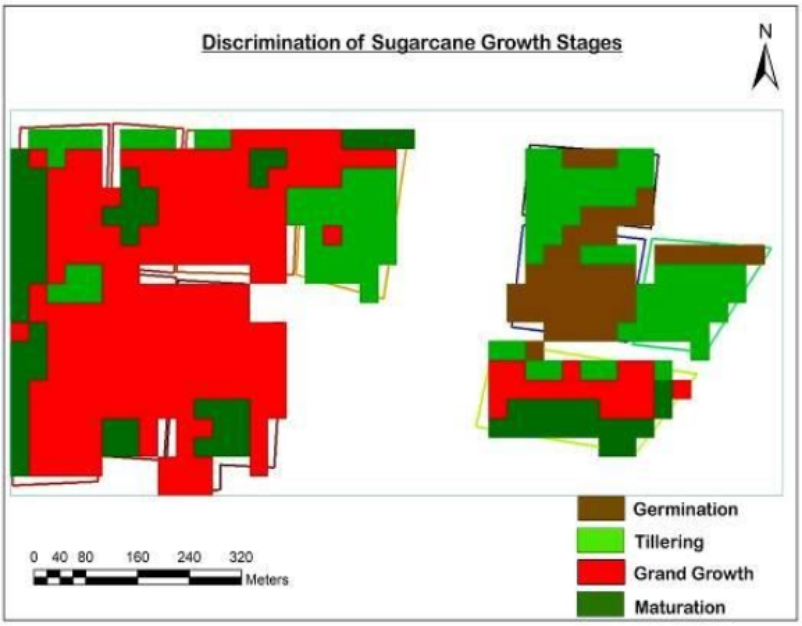
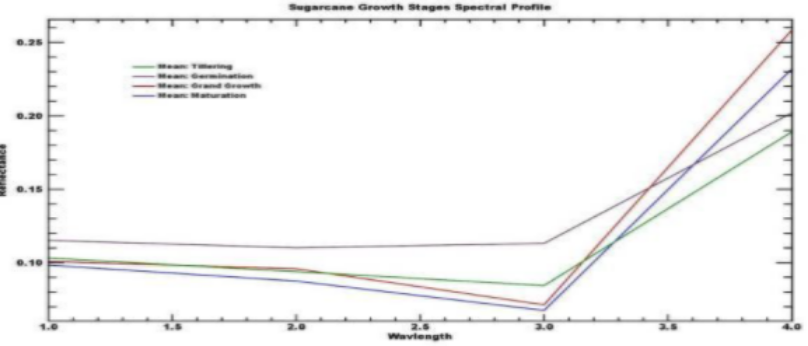
Sugarcane Phenology using Vega-GEOGLAM platform
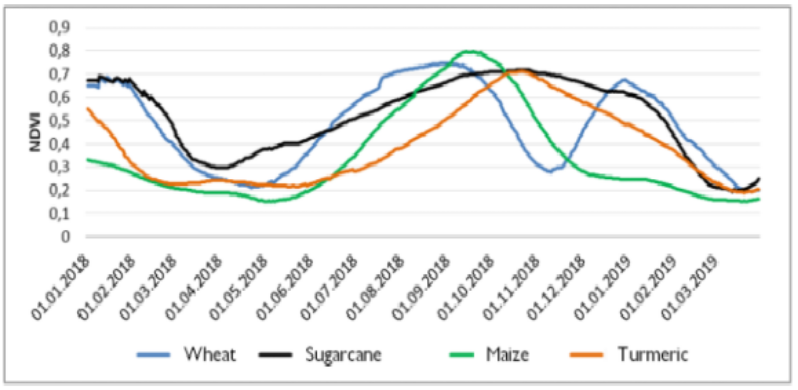
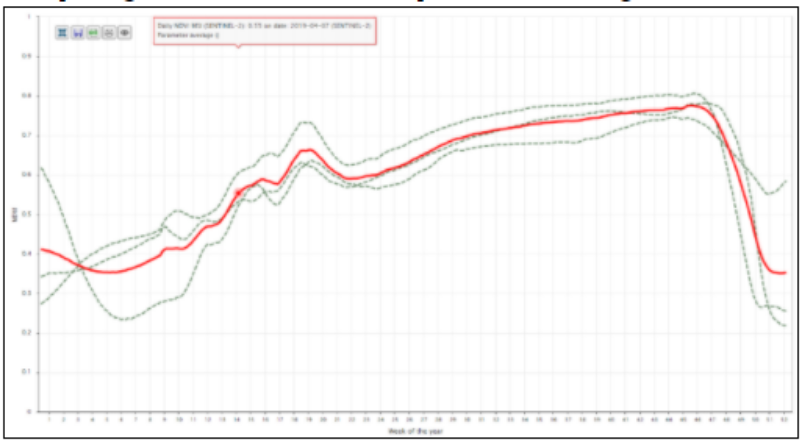
Time-series NDVI values allow tracking crop growth. time-series allows tracking crop growth on a weekly basis and reflecting the change in biomass (the ratio between RED and NIR bands). For example, fig. below shows the NDVI profiles for few sugarcane fields
7. Crop growth monitoring using Vega-Geoglam:
Time-series NDVI values allow tracking crop growth. time-series allows tracking crop growth on a weekly basis and reflecting the change in biomass (the ratio between RED and NIR bands). For example, fig. below shows the NDVI profiles for few sugarcane fields
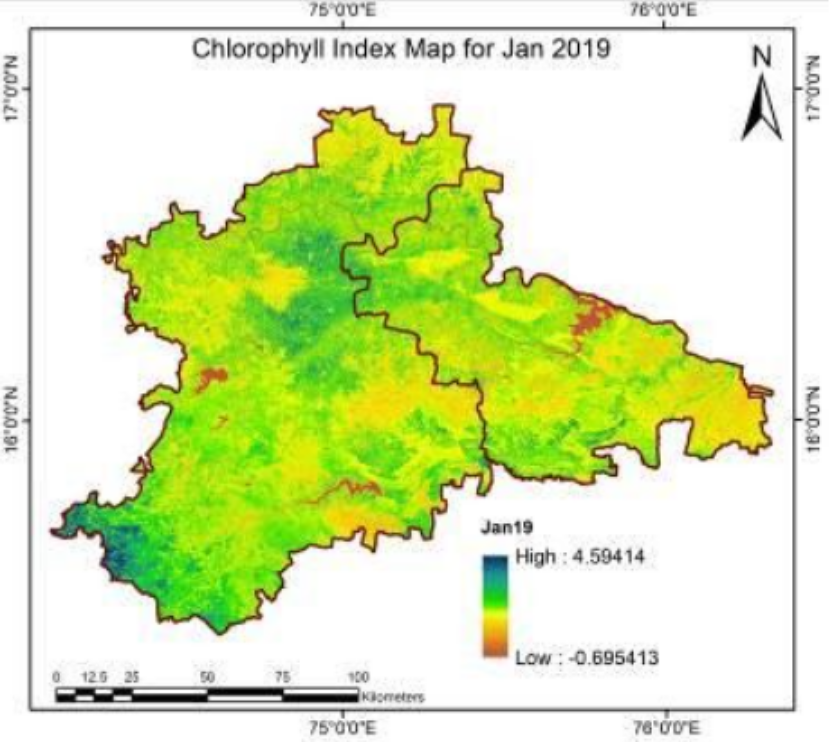
8. Chlorophyll Index Mapping
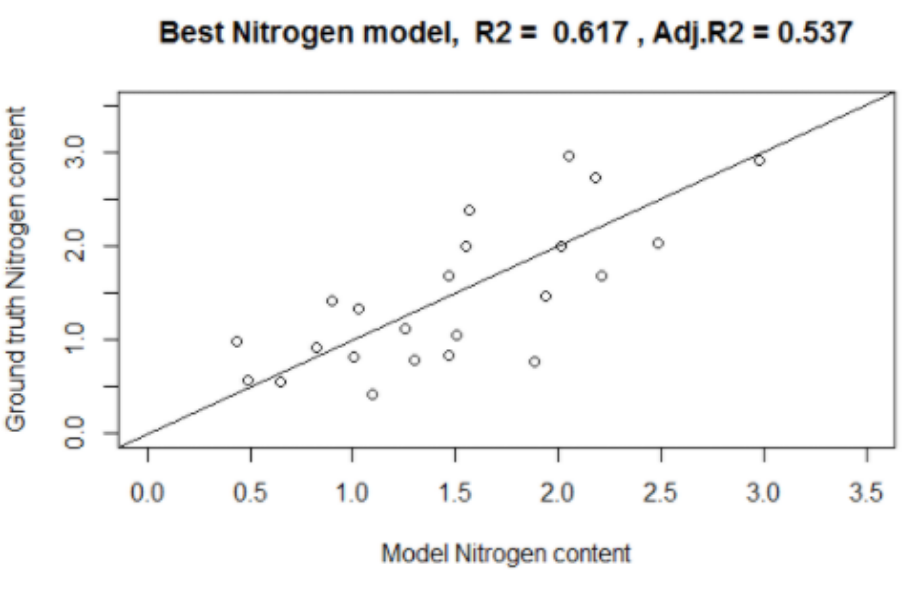
9. Nitrogen modeling
The found model for Nitrogen content estimation is N = -0.055*MCARI8A+ 2.23*MCARI5+700.08*GNDVI+237.25*GNDVI2-148.32
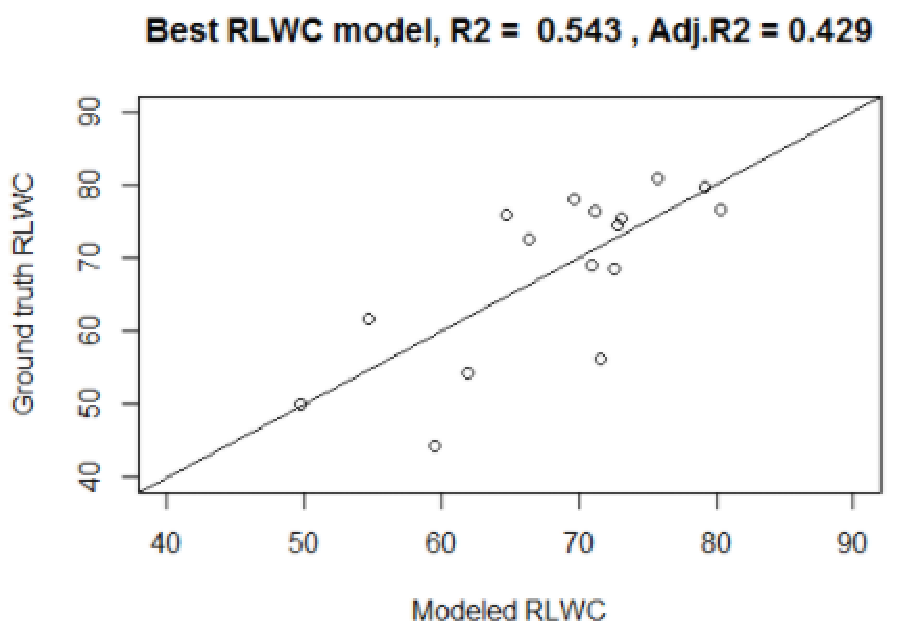
10. Relative leaf water content (RLWC) modeling
Multiple regression model was utilized for RLWC estimation. Most informative predictors such as EVI2, SAVI, NDWI, NDDI, GVMI, NMDI, and MSI are evaluated.
W=499.73*NDDI-99.76*NDWI-30.46*NDWI2-229.65